Market makers play a crucial role in financial markets by ensuring trades happen smoothly, even when buyers and sellers dont perfectly match up. They might be large financial institutions, hedge funds, or even individual traders who provide liquidity and facilitate trading activities.
But what exactly is a market maker, and how do they make money? This article takes an in-depth look at market makers, explaining their role, how they operate, and the advantages and drawbacks of having them in financial markets.
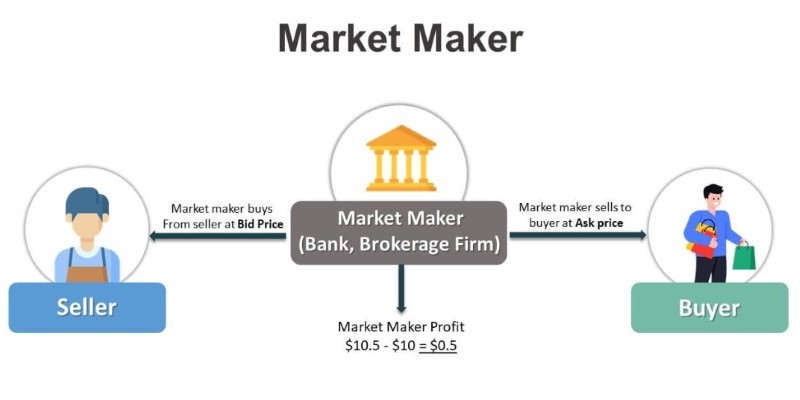
A market maker is a financial entity that continuously offers to buy and sell securities to maintain liquidity in the market. Their primary goal is to facilitate trading by quoting both a buy price (bid) and a sell price (ask) for a particular asset. The difference between these two prices is known as the spread, which is where market makers typically make their money.
Without market makers, buying and selling financial instruments would be inefficient, as matching buyers with sellers could take a long time. Market makers bridge this gap, ensuring theres always someone ready to trade, which stabilizes the market and keeps prices more consistent.
Market makers operate by constantly quoting both buy and sell prices for securities. Lets say a market maker quotes a bid price of $99 and an ask price of $101 for a stock. This means they are willing to buy the stock at $99 and sell it at $101. When a retail investor buys the stock at $101, the market maker sells it to them, and when another investor sells the stock at $99, the market maker buys it. The $2 difference between the buy and sell price represents the spread, which is the market makers profit.

Market makers need to manage their inventory effectively to avoid holding too much of a declining asset or missing out on rising markets. They use sophisticated algorithms and strategies to balance their positions and minimize risk. However, there is always an inherent risk since market conditions can change rapidly, and they could end up holding assets that lose value.
In todays markets, technology plays a critical role. Many market makers employ high-frequency trading (HFT) systems that allow them to execute trades within milliseconds. This speed is essential for capturing the best spreads and managing large volumes of trades effectively.
Liquidity Provision: Market makers ensure theres always liquidity in the market, which is crucial for smooth trading. Without them, investors might struggle to buy or sell assets quickly.
Stabilizing Prices: By consistently quoting buy and sell prices, market makers contribute to more stable prices in financial markets. This reduces large price swings, making markets less volatile.
Facilitating Smaller Investors: Market makers allow smaller investors to trade with ease, as they dont have to wait for a buyer or seller to emerge in the market.
Potential Conflicts of Interest: Market makers can sometimes engage in practices like front-running, where they use their knowledge of pending large orders to profit at the expense of other traders.
Wider Spreads in Low Liquidity: In less liquid markets or during volatile periods, market makers may widen the spreads, making it more expensive for traders to buy or sell.
Risk of Manipulation: There are concerns that market makers could manipulate prices to benefit their positions, although regulatory bodies monitor this closely to prevent it.
Market makers operate across various financial markets, including stocks, forex, and options. Their role may slightly differ depending on the market.
In stock markets, market makers are often large institutions or designated firms that ensure continuous trading for specific stocks. They work closely with exchanges like the NYSE or NASDAQ, where they must meet specific obligations to provide liquidity. Market makers in this space typically earn from the bid-ask spreads and, in some cases, receive rebates from exchanges for adding liquidity.

The forex market relies heavily on market makers because its decentralized, meaning theres no central exchange. Market makers in forex provide the bid-ask spreads and take positions against retail traders. They help maintain liquidity in a highly active and global market that operates 24/7.
In the options market, market makers are crucial because options can be complex and less liquid than regular stocks. They help price options fairly by factoring in various variables like volatility and time decay. The nature of options trading requires market makers to be highly knowledgeable and capable of managing significant risk.
Market makers are an integral part of financial markets, providing liquidity and ensuring that trades can be executed smoothly, even when buyers and sellers arent perfectly aligned. They manage inventory, utilize advanced technology, and employ sophisticated strategies to earn profits from the spread between buy and sell prices. While they play a stabilizing role, there are also some downsides, like potential conflicts of interest and the risk of market manipulation. Understanding how market makers function is key for any investor or trader looking to navigate todays complex financial markets.
In essence, market makers keep the financial ecosystem moving, balancing supply and demand across various markets while earning a profit from their role. They may not be widely known outside financial circles, but their influence on the stability and efficiency of trading is significant.

By Maurice Oliver/Aug 30, 2024

By Rick Novak/Jul 13, 2024

By Jennifer Redmond/Sep 04, 2024

By Verna Wesley/Aug 27, 2024

By Sid Leonard/Aug 26, 2024

By Korin Kashtan/Sep 04, 2024

By Madison Evans/Sep 04, 2024

By Mason Garvey/Oct 13, 2024

By Gabrielle Bennett /Sep 04, 2024

By Vicky Louisa/Sep 04, 2024

By Darnell Malan/Aug 29, 2024

By Triston Martin/Sep 04, 2024